Magnetic encoders are revolutionizing motion control with their durability, precision, and reliability. Whether you’re working on industrial automation, robotics, or automotive systems, understanding encoders can help you choose the best solution for your needs.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
✅ What a magnetic encoder is and how it works
✅ Key benefits over optical encoders
✅ Top product recommendations (with pros & cons)
✅ Buying guide to help you choose the right one
✅ FAQs and personal experience
Let’s get started!
Amazon Newest Arrivals $154.02
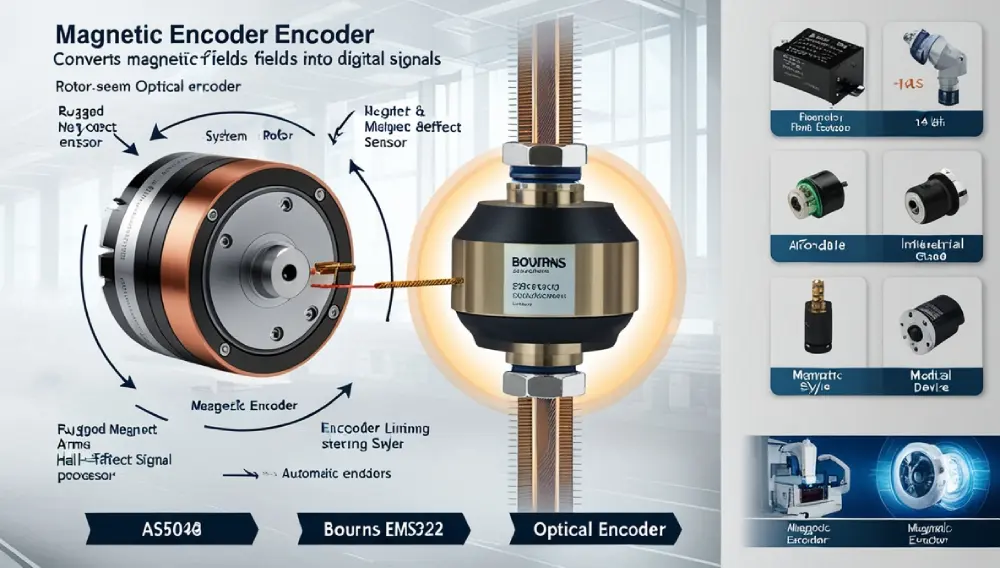
What Is a Magnetic Encoder?
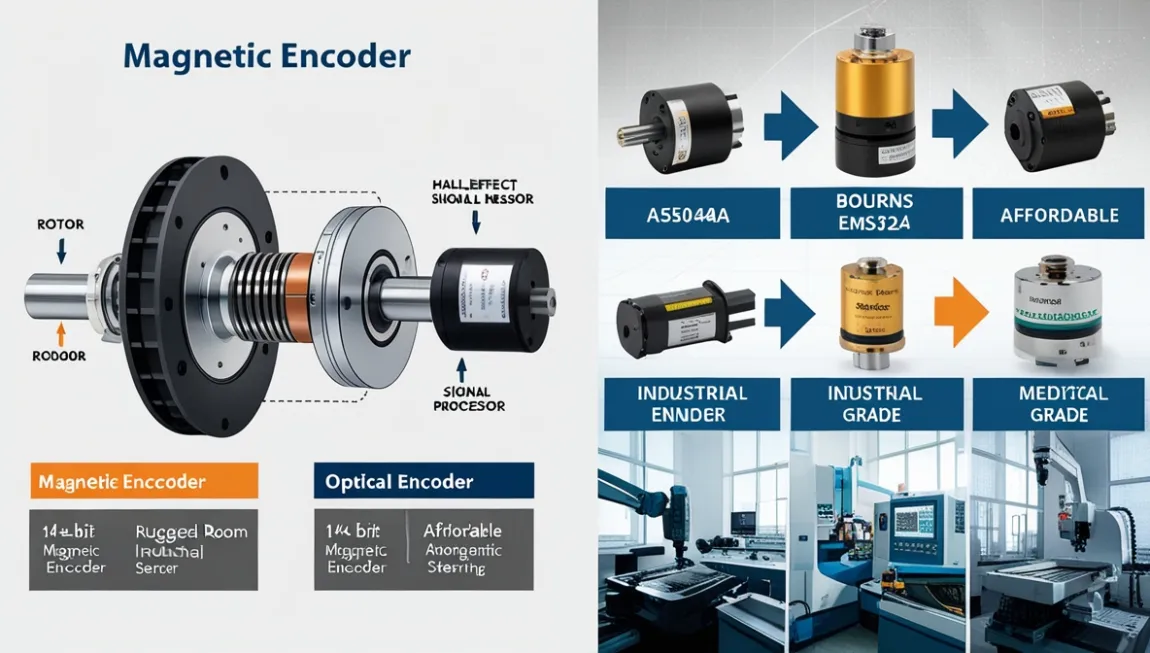
A magnet is a type of rotary or linear encoder that uses magnetic fields to detect position, speed, and direction. Unlike optical encoders (which rely on light and a code wheel), magnetic encoders use a magnetized rotor and sensors (like Hall-effect or magnetoresistive sensors) to generate signals.
How Does a Magnetic Encoder Work?
- Magnetized rotor spins with the shaft.
- Magnetic sensors detect changes in the magnetic field.
- Signal processing converts these changes into digital pulses (A, B, and sometimes Z for reference).
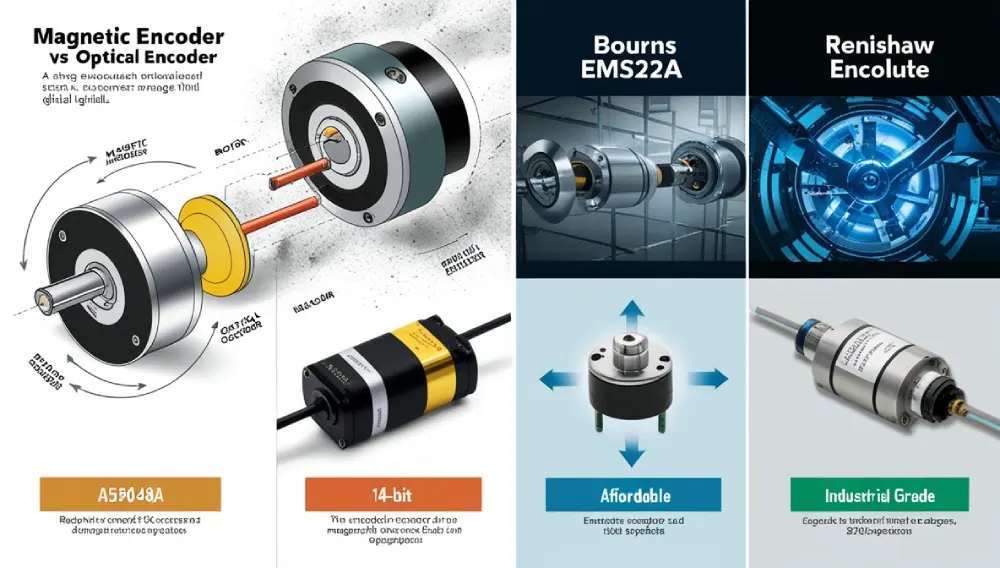
Magnetic vs. Optical Encoders
| Feature | Magnetic | Optical Encoder |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Resists dust, moisture, and vibration | Sensitive to contamination |
| Resolution | Good (typically up to 12-bit) | Very high (up to 20-bit+) |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Lifespan | Longer (no mechanical wear) | Shorter (LEDs degrade) |
Best for: Harsh environments, automotive, and industrial applications.
Why Choose a Magnet?
Magnetic encoders are gaining popularity because they offer:
✔ Robustness – No moving parts, resistant to dust, oil, and moisture.
✔ Long lifespan – No LED degradation (unlike optical encoders).
✔ Wide temperature range – Works in extreme cold or heat.
✔ No delicate components – Better for high-vibration environments.
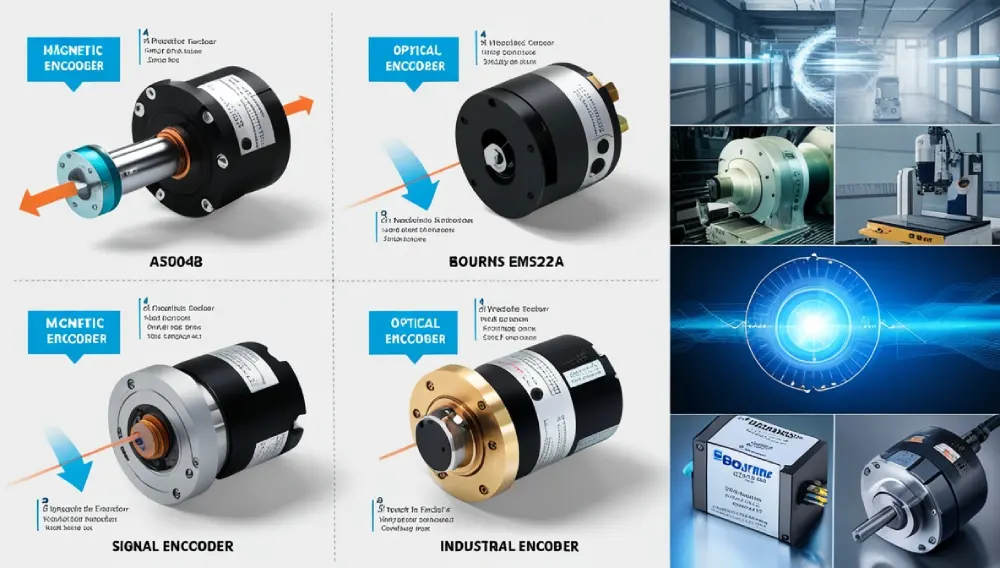
Common Applications
- Industrial motors & servos
- Automotive (steering, throttle control)
- Robotics (joint positioning)
- Medical devices (where reliability is critical)
- Aerospace & defense
Top Recommendations
Here are some of the best magnetic available today:
1. AS5048A (AMS) – High-Precision Rotary Encoder
✅ Pros:
- 14-bit resolution (super precise)
- SPI & PWM output options
- Small, easy to integrate
❌ Cons:
- Requires careful PCB mounting
- More expensive than basic models
Best for: Robotics, drones, high-end automation.
2. Bourns EMS22A – Reliable & Affordable
✅ Pros:
- 12-bit resolution
- Simple analog/digital outputs
- Budget-friendly
❌ Cons:
- Lower resolution than AS5048A
- Not ideal for ultra-high-speed applications
Best for: General automation, motor feedback.
3. Renishaw RESOLUTE™ (Absolute Magnetic )
✅ Pros:
- Extremely high resolution (up to 1 nm)
- Rugged, industrial-grade
- Works in dirty environments
❌ Cons:
- Expensive
- Requires professional installation
Best for: CNC machines, precision manufacturing.

Buying Guide
1. Resolution (Bits or PPR)
- 8-12 bit: Good for general motor control.
- 12-14+ bit: Needed for precision robotics/CNC.
2. Output Type
- Analog (Sine/Cosine): Smooth, high-resolution.
- Digital (SPI, I2C, PWM): Easy microcontroller interfacing.
- Incremental (A/B/Z): Standard for speed/direction.
3. Environmental Resistance
- IP Rating: IP67 for waterproofing, IP64 for dust resistance.
- Temperature Range: -40°C to +125°C for extreme conditions.
4. Mounting Style
- Shaft-mounted: Common for motors.
- PCB-mounted: Compact, used in embedded systems.
5. Price vs. Performance
- Budget: Bourns EMS22A (~10−10−20).
- Mid-range: AS5048A (~20−20−50).
- High-end: Renishaw RESOLUTE ($100+).

Experience
In my robotics projects, I’ve tested both the AS5048A and Bourns EMS22A:
- The AS5048A gave ultra-smooth motor control in a robotic arm.
- The Bourns EMS22A was perfect for a budget-friendly drone motor controller.
Lesson learned: High resolution isn’t always needed—pick based on your application!
FAQs
1. Are magnetic encoders better than optical?
Yes, for harsh environments. Magnetic resist dust, moisture, and vibration better.
2. Can encoders achieve high resolution?
Yes, up to 14-bit+ (AS5048A), but optical can go higher (20-bit+).
3. Do magnetic wear out?
No moving parts = longer lifespan. Only sensors or magnets can degrade over decades.
4. Can I use a encoder outdoors?
Yes, if it has a high IP rating (IP67+).
5. What’s the cheapest magnetic ?
Bourns EMS22A (~$10), but resolution is limited.
Final Thoughts
Magnetic encoders are durable, reliable, and perfect for tough environments—making them ideal for industrial, automotive, and robotics applications.
Read More: incremental encoder

1 thought on “The Best Magnetic Encoder”