Introduction
Imagine a world where robots perform surgery with unerring precision, drones navigate stormy skies without faltering, and factories hum with machines that never miss a beat. This isn’t a distant future—it’s the reality powered by servo motors, the unsung heroes of modern automation. Whether you’re a student building your first robot, an engineer optimizing industrial machinery, or a hobbyist crafting a smart home gadget, understanding servo motors is your gateway to precision control.
By the end of this guide, you’ll:
- Master the mechanics of servo motors and their closed-loop magic.
- Compare types like BLDC, AC, and micro servo motors for your needs.
- Avoid pitfalls like overheating or misalignment with pro tips.
- Unlock real-world applications from aerospace to DIY projects.
Let’s dive deep—no PhD required!
What is a Servo Motor?
A servo motor is a self-aware powerhouse. Unlike ordinary motors that spin blindly, servo motors use real-time feedback to adjust their position, speed, or torque. Think of it as a GPS-guided engine: it knows exactly where it is, where it needs to go, and how to course-correct instantly.
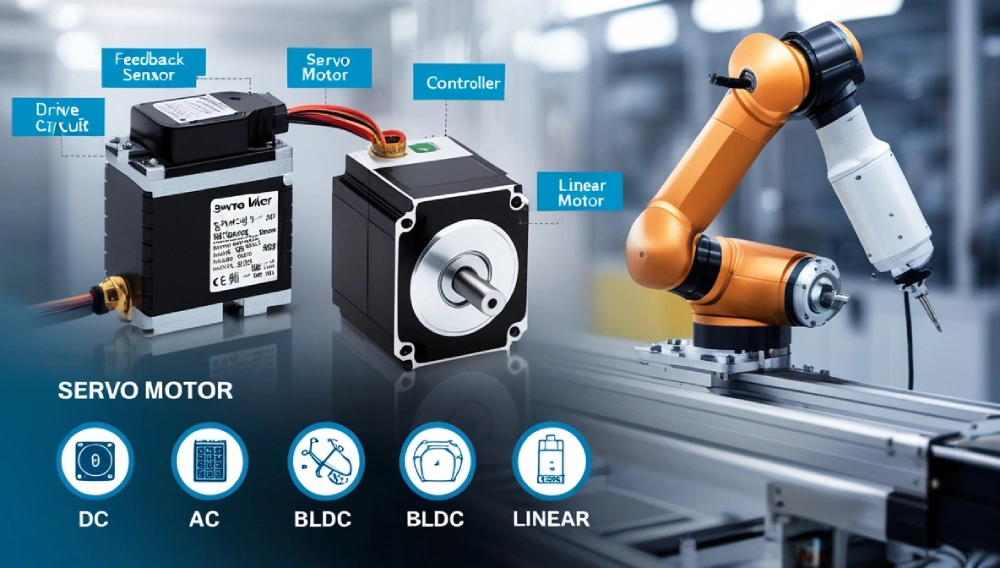
Core Components:
- Motor: The muscle (DC, AC, or brushless).
- Controller: The brain sending commands. e.g. Arduino
- Feedback Sensor: The eyes (encoder, potentiometer) tracking performance.
- Drive Circuit: Amplifies signals to power the motor.
Real-World Analogy:
It’s like a self-driving car that adjusts steering, acceleration, and braking to stay perfectly in lane—no human intervention needed!

How Servo Motors Work: The Science Made Simple
- Command Input: You set a target ( “Rotate 90 degrees”).
- Motion Starts: The motor begins moving toward the goal.
- Feedback Loop: Sensors monitor progress and report deviations.
- Adjustment: The controller tweaks voltage, current, or pulse width to hit the target.
Why This Matters:
Servo motors eliminate guesswork. For example, in a 3D printer, they ensure layers align perfectly—no gaps or misprints.
Types of Servo Motors: Which One Fits Your Project?
1. DC Servo Motors
- Best For: Budget-friendly DIY projects, small robotics.
- Example: TowerPro SG90 ($5, Arduino-compatible).
- Pros: Affordable, lightweight, easy to control.
- Cons: Limited torque, shorter lifespan under heavy use.
Read more about DC Servo Motors!
Pro Tip: Love tinkering? Start with a micro servo motor (like MG90S) for under $10.
2. AC Servo Motors
- Best For: Industrial machinery (CNC, conveyor belts).
- Example: Yaskawa SGM7G (handles 1,000+ hours of continuous operation).
- Pros: High torque, durable, ideal for heavy loads.
- Cons: Expensive, requires complex controllers.

3. BLDC Servo Motors (Brushless)
- Best For: High-speed, low-maintenance tasks (drones, EVs).
- Example: T-Motor MN5208 (used in racing drones).
- Pros: Energy-efficient, long lifespan, minimal heat.
- Cons: Higher cost, needs specialized drivers.
Read More about BLDC Servo Motors!
4. Linear Servo Motors
- Best For: Straight-line motion (3D printers, automated doors).
- Example: Hiwin LSA Series.
- Pros: No gears = zero backlash, ultra-smooth motion.
- Cons: Limited to linear paths, higher cost.
5. Micro Servo Motors
- Best For: Hobby projects (RC cars, camera gimbals).
- Example: MG90S (metal gears for durability).
- Pros: Compact, affordable, easy to integrate.
- Cons: Limited torque (5-10 kg/cm).
Read More about Micro Servo Motors!
Servo Motors vs. Stepper Motors: The Ultimate Face-Off
| Factor | Servo Motors | Stepper Motors |
| Control System | Closed-loop (self-correcting) | Open-loop (no feedback) |
| Precision | ±0.1° accuracy | ±1.5° (prone to missed steps) |
| Speed | Up to 5,000 RPM | Up to 1,200 RPM |
| Torque at Speed | Maintains torque at high speeds | Torque drops as speed increases |
| Cost | 20−20−500+ | 5−5−200 |
| Best For | Robotics, CNC, aerospace | 3D printers, basic automation |
Key Takeaway:
- Choose Servo Motors for precision tasks (surgical robots).
- Choose Stepper Motors for cost-sensitive, low-speed projects (conveyor belts).
Still Confused? Dive deeper: Servo vs. Stepper Motors: Which Wins for Your Project?
Applications of Servo Motors: From Factories to Your Living Room
1. Industrial Automation
- CNC Machines: AC servo motors cut metal with 0.001mm precision.
- Packaging Lines: BLDC motors fill, seal, and label 100+ products/minute.
- Textile Machinery: M92 Juki servo motors stitch denim 2x faster than clutch motors.
2. Robotics
- Robotic Arms: Six-axis arms use 6+ servo motors for welding, painting, and assembly.
- Humanoid Robots: Micro servo motors mimic human joint movements.
3. Aerospace
- Satellites: BLDC motors adjust solar panels to maximize energy capture.
- Drones: Lightweight servos stabilize cameras and adjust propeller pitch.
4. Consumer Tech
- Camera Gimbals: Micro servos keep footage steady while hiking or biking.
- Smart Homes: Linear servos automate blinds, locks, and pet feeders.
5. Automotive
- Electric Vehicles: BLDC motors control throttle response and regenerative braking.
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): Servos adjust steering and braking in real time.
How to Choose the Right Servo Motor: A 7-Step Guide
1. Define Your Application
- Precision Tasks ( robotic surgery): Closed-loop BLDC motors.
- Heavy Loads (CNC machines): High-torque AC servo motors.
- Hobby Projects (Arduino robots): Micro DC servo motors.
Check Out
2. Calculate Torque & Speed Requirements
- Torque Formula: Torque (Nm)=9.5488Force (N)×Radius (m)
- Example: A robotic arm lifting 5kg at 0.1m radius needs ~0.5 Nm torque.
3. Match Power Supply
- DC Motors: 5V-12V (Arduino-friendly).
- AC Motors: 110V-240V (industrial setups).
4. Check Feedback Resolution
- Encoders: 12-bit (4,096 steps) for high precision.
- Potentiometers: 10-bit (1,024 steps) for basic tasks.
5. Environment-Proofing
- IP Ratings: IP65 for dust/water resistance.
- Temperature: -20°C to 80°C for most models.
6. Budget Considerations
- Hobbyists:
- 5−50 (e.g., SG90, MG996R).
- Professionals:
- 200−1,000+ (e.g., Yaskawa, Allen-Bradley).
7. Brand & Support
- Top Brands:
- Faulhaber: Precision micro motors.
- Yaskawa: Industrial-grade AC servos.
- T-Motor: BLDC motors for drones.
Installation & Maintenance: Pro Tips for Peak Performance
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
- Mounting:
- Use anti-vibration brackets to reduce noise.
- Alhaftach motors parallel to the load axis to prevent binding.
- Wiring:
- Power: Red (+) to power supply, Black (-) to ground.
- Signal: Orange/Yellow to PWM pins (Arduino, Raspberry Pi).
- Calibration:
- Use software like RoboDK or Arduino IDE to set zero position.
- Testing:
- Run at 50% load initially to check for overheating or jitter.
Maintenance Checklist
- Daily: Listen for unusual noises (grinding = worn gears).
- Monthly: Clean vents with compressed air.
- Annually: Replace grease in gearboxes (if applicable).
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Problem | Cause | Fix |
| Motor Jitters | Loose wiring | Secure connections |
| Overheating | Overloading | Reduce load or add cooling fan |
| No Movement | Dead power supply | Test with multimeter |
| Inaccurate Stops | Faulty encoder | Recalibrate or replace sensor |
FAQs: Your Servo Motor Questions, Answered
No! Servo motors rely on controllers (Arduino, PLC) to send PWM signals.
For precision, yes! Servo motors self-correct; DC motors run open-loop.
5-10 years with proper maintenance. BLDC motors often outlast brushed types.
Most standard servos rotate 180°, but continuous rotation servos (Parallax) spin freely.
It’s “hunting” for position—recalibrate or reduce mechanical resistance.
The Future of Servo Motors: Trends to Watch
- AI Integration: Motors that learn and adapt to load changes.
- IoT Connectivity: Remote monitoring via apps ( diagnose issues from your phone).
- Eco Designs: Energy recovery systems that feed excess power back to the grid.
Conclusion: Ready to Harness Servo Power?
Servo motors are the quiet revolutionizers of automation, transforming industries and hobbies alike. Whether you’re retrofitting a sewing machine with an M92 Juki motor or building a Mars rover prototype with micro servos, the right choice ensures flawless performance.
Your Next Steps:
- Explore: Browse servo motors on ServoCity or Amazon.
- Learn: Master PWM control with our Arduino Servo Guide.
- Connect: Join forums like Reddit’s r/robotics for expert advice.
Read More,
Motor Drivers for Servo Motors,
Servo Motor vs Stepper Motor Comparison,
Servo Motors vs Regular Motors
About the Author:
John Carter is a robotics engineer with 12+ years of experience. She’s designed servo systems for NASA rovers and now runs a YouTube channel teaching DIY automation.
Loved This Guide? Share it with your colleagues, students, or maker community!


16 thoughts on “Servo Motors | Applications| Mastery and Where to Buy the Best”