Introduction
A stepper motor linear actuator is a device that combines the functionality of a stepper motor with a linear motion mechanism. This allows for precise control of movement along a straight path, making it popular in various applications such as robotics, CNC machines, and automation systems. Whether you are an engineer, technician, DIY enthusiast, or a student, understanding how this technology works can enhance your projects and designs. In this article, we will explore what a stepper motor linear actuator is, how it operates, its components, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and what to consider when buying one.
2. What Is a Stepper Motor Linear Actuator?
In simple terms, a stepper motor linear actuator is a device that converts rotational motion into linear motion. It consists of a stepper motor that drives a lead screw or ball screw, which in turn moves a platform or load in a straight line.
Technical Definition
From a technical standpoint, a stepper motor is an electric motor that divides a full rotation into a series of discrete steps. This allows for precise positioning and control. When combined with a linear motion mechanism, it enables accurate movement in one direction.
3. How It Works (Mechanism Explained)
The operation of a stepper motor linear actuator involves several key components working together:
- Stepper Motor: This motor receives electrical pulses from a controller, which dictates how far and how fast it should turn.
- Lead Screw or Ball Screw: This component translates the rotational motion of the motor into linear motion. As the screw turns, it moves a nut that is attached to the load.
Torque and Step Resolution
The torque produced by the stepper motor is crucial for determining how much weight the actuator can move. Additionally, the step resolution, or how many steps the motor can take in one full rotation, affects the precision of the movement.
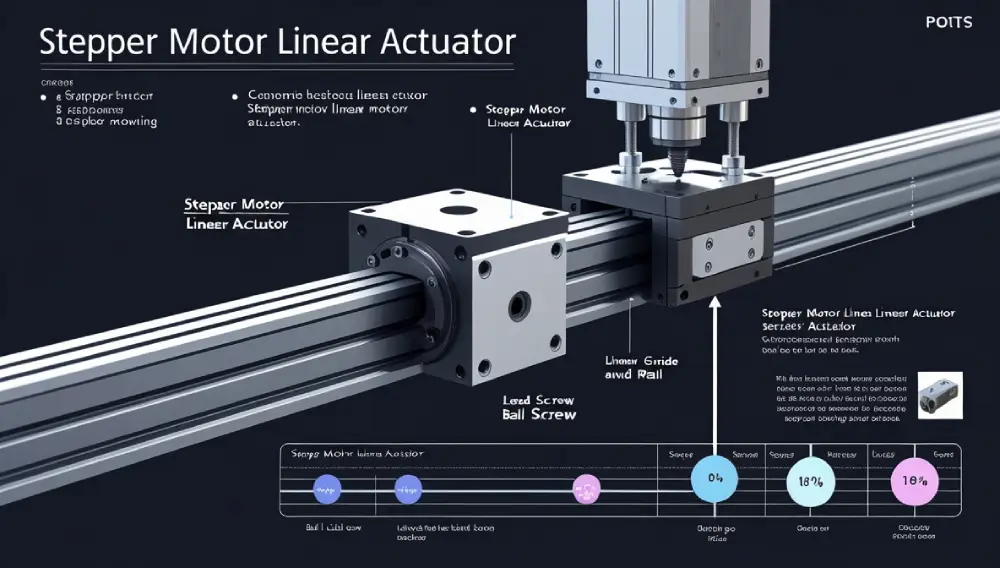
4. Key Components
Understanding the parts of a stepper motor linear actuator can help you appreciate how it functions:
- Stepper Motor: The heart of the actuator, providing the necessary rotational force.
- Lead Screw or Ball Screw: Converts the motor’s rotation into linear motion.
- Linear Guide/Rail: Ensures smooth and straight movement of the actuator.
- Couplers and Housing: Connects the motor to the screw and protects the internal components.
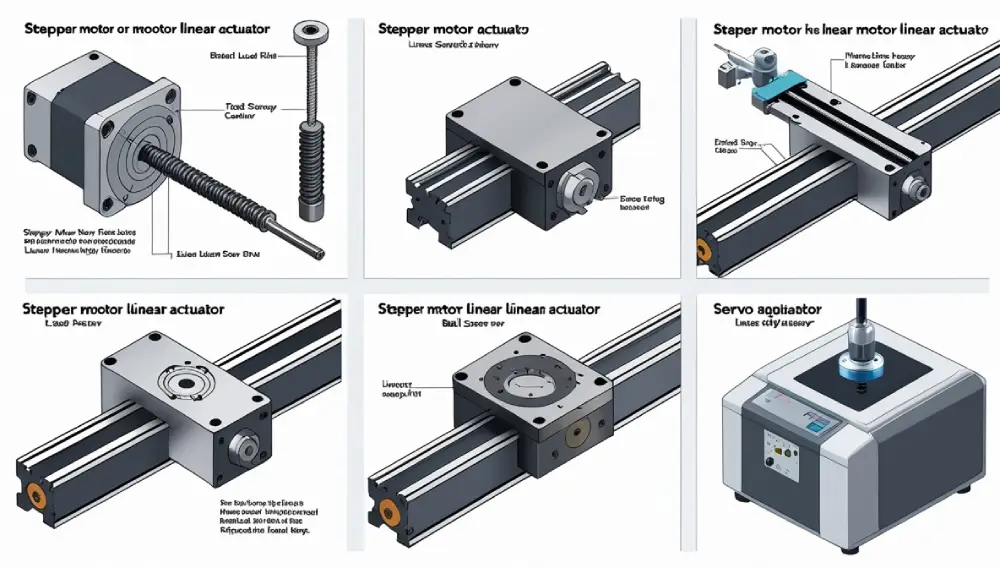
5. Applications
Stepper motor linear actuators are versatile and used in various fields:
- CNC Machines: For precise cutting and shaping of materials.
- 3D Printers: To control the movement of the print head or build platform.
- Medical Devices: For accurate positioning in diagnostic equipment.
- Robotics: To enable controlled movement in robotic arms.
- Precision Positioning Systems: For applications requiring exact placement.
6. Advantages and Disadvantages
Pros
- Precision: Offers high accuracy in positioning.
- Repeatability: Can consistently return to the same position.
- Easy Control: Simple to operate with microcontrollers.
Cons
- Speed Limitations: Not as fast as some other types of actuators.
- Resonance: Can produce vibrations at certain speeds.
- Cost: May be more expensive than basic DC motors.
7. Buying Guide: What to Look For
When purchasing a stepper motor linear actuator, consider the following factors:
- Stroke Length: The distance the actuator can move.
- Step Angle/Resolution: Determines the precision of the actuator.
- Holding Torque: The amount of weight the actuator can hold when stationary.
- Speed (mm/s): How fast it can move.
- Compatibility with Driver/Controller: Ensure it works with your existing setup.
8. Top Models to Consider
Here are a few popular models to look into:
- Model A: Specifications: 200mm stroke, 1.8° step angle, 5 kg holding torque.
- Model B: Specifications: 300mm stroke, 0.9° step angle, 10 kg holding torque.
- Model C: Specifications: 150mm stroke, 1.8° step angle, 3 kg holding torque.
9. Stepper vs Servo in Linear Actuation
| Feature | Stepper Motor Linear Actuator | Servo Motor Linear Actuator |
| Precision | High | Very High |
| Speed | Moderate | High |
| Control | Open-loop | Closed-loop |
| Cost | Generally Lower | Higher |
When to Choose One Over the Other
Choose a stepper motor for applications requiring precision and simplicity. Opt for a servo motor when speed and feedback control are critical.
10. How to Control a Linear Stepper Actuator
Controlling a stepper motor linear actuator can be done using:
- Microcontrollers: Such as Arduino or Raspberry Pi.
- Stepper Drivers: Like A4988, TMC2209, or DRV8825.
11. Conclusion
In summary, a stepper motor linear actuator is a powerful tool for achieving precise linear movement. Whether you are building a CNC machine, a 3D printer, or a robotic arm, understanding its components and functionality can greatly enhance your projects. Remember to consider factors like stroke length, holding torque, and compatibility when making your purchase.
12. FAQ Section
A stepper motor is a type of motor that moves in steps, while a linear actuator converts rotational motion into linear motion.
Yes, a stepper motor linear actuator is designed specifically to move in a straight line.
Stepper linear actuators are highly accurate, often achieving precision within a few micrometers.
It depends on your needs: stepper motors are great for precision and simplicity, while servo motors excel in speed and feedback control.
By understanding the workings and applications of stepper motor linear actuators, you can make informed decisions in your engineering projects and DIY endeavors. Happy building!


1 thought on “What Is a Stepper Motor Linear Actuator? How It Works & What to Consider”